
A power cable is an electrical cable, an assembly of one or more electrical conductors, usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of electrical power. Power cables may be installed as permanent wiring within buildings, buried in the ground, run overhead, or exposed. Power cables that are bundled inside thermoplastic sheathing and that are intended to be run inside a building are known as NM-B (nonmetallic sheathed building cable).
Types of Power Cables
A power cable is a type of electrical cable used to transmit electricity. Power cable types composed of a conductor ( typically made of copper or aluminum) and an insulation layer. Typically, the electrical power cable is installed in buildings and other structures to supply electricity.
Nonelectrical power cable types are also used for other purposes, such as connecting portable devices and aerial bundled cables (ABC) for overhead power lines. There are different power cables types based on their intended application, conductor material, insulation material, and cross-sectional area.

Considering the various types of power cables is essential for several reasons. It can help you better understand each type’s capabilities and limits. Additionally, knowing the different power cables types can also aid in troubleshooting should an issue ever arise. Electrical power cable types are classified as:
- Low Voltage Cable:
These are compatible with 0.6/1KV electricity systems. PVC-insulated cable is the most popular low-voltage wiring type. Copper or aluminum is used as the conductor. Low voltage cables are often used in homes and businesses, including powering lights, outlets, and appliances.
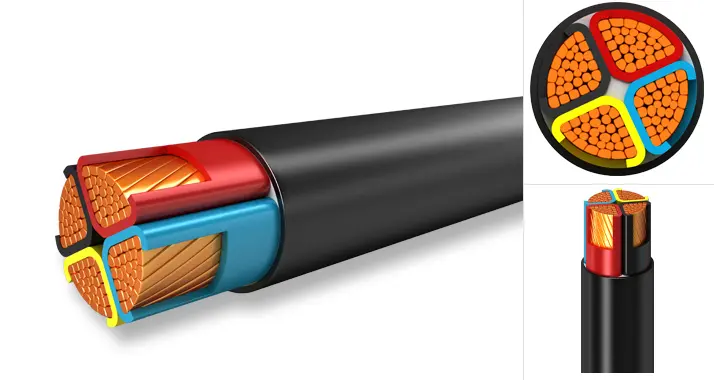
Typically, low-voltage cables are made from copper or aluminum. The former is a more expensive option but is also more durable and has better electrical conductivity. On the other pointer, aluminum is less pricey but not as durable and has poorer electrical conductivity.
- Medium Voltage Cable:
As the name implies, medium voltage cables are designed for use with systems with a voltage of between 600 and 69,000 volts. The most common medium voltage cable type is XLPE, which stands for Cross-Linked Polyethylene. Medium voltage cables are typically used in industrial applications, such as powering large motors or connecting different buildings.
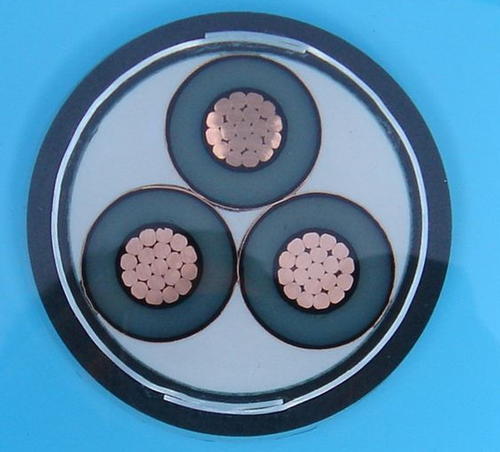

Medium voltage standard power cable types are usually high-quality copper or aluminum. These metals are used because of their excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion. The electrical current flowing through the medium voltage cable produces a lot of heat, so the copper or aluminum must be able to withstand these high temperatures.
- High Voltage Cable:
High voltage cables are designed for use with systems with 69,000 volts or more. The most common high voltage cable type is EPR, which stands for Ethylene Propylene Rubber. High voltage cables are used in utility applications, such as connecting power plants to substations. These power cables have extensive use in industries.
Industrial power cable types are usually high voltage cables. The main reason for this is that the higher the voltage, the less electrical current is required to power the same amount of equipment. This means less heat is generated, making it easier to manage and control. Another reason why high voltage cables are used in industrial applications because they are less likely to experience power outages.
- Flexible Cable:
Flexible power cable types are designed to be used in applications where the cable needs to be bent or twisted. The most common flexible cable type is PVC, which stands for Polyvinyl Chloride. Flexible cables are often used in electronic equipment, such as laptops and cell phones.
The flexibility needs to be considered when selecting the type of metal to use. If the application requires a lot of flexibility, then a metal with a lower modulus of elasticity, such as copper, is typically used. If the application does not require as much flexibility, a metal with a higher modulus of elasticity, such as steel, can be used.

























